Exploring the Impact of AI Agents: Revolutionizing Modern Industries and Everyday Life
Exploring the World of the AI Agent
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
Key Takeaways
- AI agents are autonomous software systems that learn from feedback and adapt over time.
- They rely on techniques like machine learning and natural language processing.
- Their real-world applications span e-commerce, healthcare, finance, and more.
- Challenges include data privacy, bias, and resource demands.
- Continued advancements point toward higher autonomy and multi-agent collaboration.
Table of Contents
- The Exciting Rise of the AI Agent in Today’s Tech Landscape
- 1. Understanding AI Agents
- 2. Key Characteristics and Components of AI Agents
- 3. Types of AI Agents
- 4. Applications of AI Agents
- 5. Advancements and Trends
- 6. Challenges in Deployment
- 7. Conclusion
- FAQ
The Exciting Rise of the AI Agent in Today’s Tech Landscape
The term “AI agent” has been on everyone’s lips lately. These powerful autonomous software systems are shaking up industries and fueling new waves of innovation around the globe. In this blog post, we dive into the world of the AI agent, exploring what these agents are, how they work, and why they are transforming everything from customer service to manufacturing. Prepare to be amazed by examples of AI agents accomplishing tasks with minimal human supervision, all while continuously learning and improving.
Let’s discover how AI agents are driving us further into the digital transformation with AI and how they could change the way we work and live.
1. Understanding AI Agents
AI agents are “autonomous software systems designed to perceive their environment, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific goals.” They often rely on technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and advanced decision-making frameworks. Over time, these agents can become more intelligent as they learn from the feedback generated by the actions they take.
Just like a self-driving car navigates roads and reacts to unexpected events, an AI agent in a different context might process a user’s query online, learn from that interaction, and then adapt how it serves future users. By applying machine learning, these agents consistently refine their strategies to deliver better results. Below, we’ll examine some of the most important characteristics and components of AI agents, as well as the tasks they can handle.
2. Key Characteristics and Components of AI Agents
According to leading technology resources, several features set AI agents apart from traditional software. Let’s explore these characteristics in detail:
a) Autonomy
AI agents do not need constant human oversight. They are often able to “work independently, require minimal human intervention, and initiate actions based on predefined goals or real-time feedback.” This gives them the freedom to perform tasks automatically, even if those tasks are repetitive or increasingly complex over time.
b) Perception
AI agents gather data from their environment. This could be through sensors, or through digital inputs like user questions posted in an online forum. Using these inputs, the agent “collects data from their environment using sensors or software inputs, such as customer queries or sensor data from devices.” By perceiving the world around them, AI agents can build a detailed understanding of relevant information—or at least enough data to make informed decisions.
c) Reasoning
AI agents use various techniques to interpret the data they gather. This includes machine learning algorithms, pattern recognition systems, and optimization methods. Through these processes, “they analyze collected data to make rational decisions, often incorporating techniques like machine learning for optimization and improvement.” For instance, if you have an AI agent that sorts incoming emails for a customer service team, it might learn how to recognize the overall sentiment of messages or classify them based on certain trigger words.
d) Action
Once an AI agent has made a decision, it follows through with an action. This might be “responding to queries, adjusting processes, or executing commands.” For example, a proactive customer service agent might automatically respond to routine questions—like store hours or return policies—whereas a manufacturing-focused AI agent might control robotic arms on a factory floor.
e) Learning
One of the most groundbreaking features of AI agents is their capacity to “improve their performance over time by learning from past experiences and outcomes.” This means that the longer these agents run, the more refined they become at performing the tasks they are assigned. For instance, a learning agent responsible for medical diagnoses might become better at interpreting images the more scans it reviews.
f) Communication
AI agents often need to communicate. They do this with users, other AI agents, or external systems. They frequently depend on “natural language processing and APIs” to complete their tasks. This allows for seamless integration with chat interfaces, websites, and other software platforms.
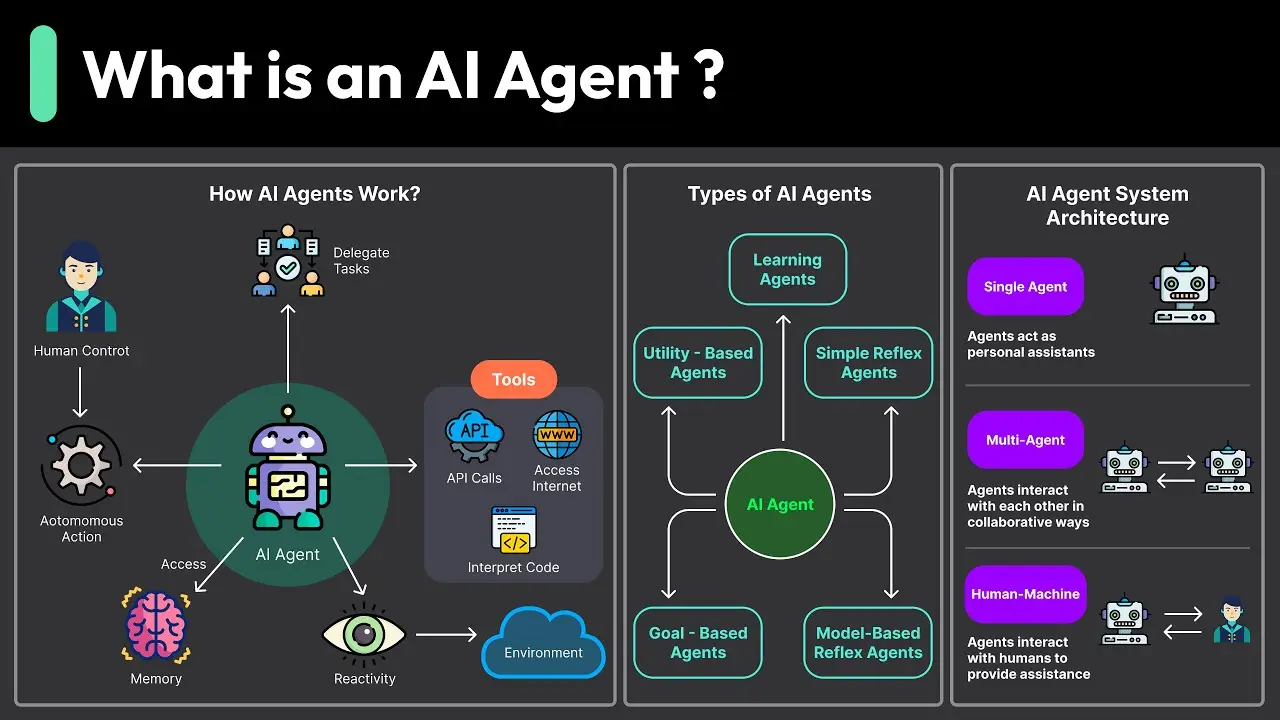
3. Types of AI Agents
AI agents can be categorized by their complexity and the goals they pursue. Below are some primary types:
1) Reactive Agents
These AI agents respond in real time to immediate inputs and do not maintain a memory of prior events. An example is a basic thermostat adjusting a room’s temperature based on the temperature reading it perceives at any given moment.
2) Proactive Agents
Practical for more advanced scenarios, these AI agents plan and carry out multi-step tasks to achieve long-term objectives. They are often seen as “virtual assistants” capable of tasks like booking appointments or making travel arrangements. They are sometimes referred to as “agents that plan and execute multi-step tasks to achieve long-term goals.”
3) Utility-based Agents
These agents make decisions according to a utility or reward function. They aim to maximize whatever metric is assigned to them—for example, profit or energy efficiency. They are especially valuable in dynamic pricing systems, allowing companies to quickly adjust product prices in response to changes in demand or market trends.
4) Learning Agents
As the name suggests, learning agents continuously refine their decision-making by incorporating feedback from the environment. Over time, they become more accurate and efficient at their tasks. This category of agent is quite common across applications, from customer support bots to more specialized technologies like healthcare imaging systems. They draw on existing knowledge to “improve their decision-making and reasoning through iterative learning from environmental feedback.”
4. Applications of AI Agents
AI agents are driving digital transformation with AI across a variety of fields. From e-commerce platforms that suggest products, to finance systems that screen for fraudulent transactions, there are endless ways to use these clever systems.
a) E-Commerce
Businesses are harnessing AI agents to give online shoppers personalized product suggestions, automatically handle simple customer queries, and speed up the checkout flow. According to trusted case studies, “AI agents provide personalized product recommendations, automate shopping tasks, and streamline customer support.” A major example is Amazon, where “the company’s recommendation system generates 35% of its revenue through AI-driven suggestions.”
b) Customer Support
Advanced AI agents can serve as customer service representatives, resolving issues faster than many humans. These autonomous chatbots and call center agents “handle complex queries, automate transactions, and reduce support tickets significantly.” A real-world example is Chatbase, whose agents “handle technical support issues, lowering support tickets by 65%.”
c) Healthcare
Medical facilities rely on AI agents to help doctors and nurses make quicker, more accurate decisions. For instance, an AI agent might read medical scans to detect abnormalities. “AI agents assist in diagnostics (e.g., analyzing medical images), create treatment plans, and guide robotic surgeries.” One famous example is Google’s AI agent for dermatology, which “outperformed dermatologists in diagnosing skin cancer with 85.4% sensitivity.” By combining machine learning and imaging data, the agent raises hopes of more timely and accurate diagnoses.
d) Manufacturing
In factories, AI agents optimize production lines and manage robotic process automation. “They optimize production processes, predict equipment failures, and control robotic systems to enhance productivity and reduce downtime.” A compelling case is Siemens, which “reduced downtime by 40% with predictive AI agents.” These agents use real-time data to forecast machinery performance and schedule maintenance, saving both time and money.
e) Finance
Fraud detection and credit scoring are prime uses of AI agents. By ingesting vast amounts of financial data, these agents learn to spot suspicious patterns and automatically flag high-risk transactions. They also “enhance fraud detection, assess creditworthiness, and streamline investment management.” JP Morgan’s COIN platform is a standout example, as it “uses AI to process lengthy legal documents efficiently.” Freeing staff from stacks of paperwork, it helps the bank handle more documentation in less time.
f) Transport
Whether it’s flying drones to deliver packages or self-driving cars navigating city streets, AI agents are essential for real-time decision-making. They provide navigation guidance, route optimization, and hazard detection. “Autonomous vehicles, powered by AI agents, integrate real-time decision-making for navigation and safety.” Waymo is a leading example, as “companies like Waymo use agents for self-driving cars operating in urban environments.”
g) Marketing and Sales
Marketing teams are turning to AI agents to nurture customer leads and identify untapped markets. These agents keep track of consumer preferences and market trends, all to deliver the right message at the right time. They automate lead generation, market analysis, and customer engagement for improved ROI. By reducing repetitive tasks, these tools free marketers to work on strategy and creative concepts.
h) Retail
For in-store and online retailers, AI agents can enhance shopping experiences through real-time inventory checks, dynamic pricing, and hyper-focused ad targeting. “AI agents dynamically adjust pricing, analyze customer behavior, and enhance shopping experiences.” Imagine walking through a store while a digital assistant instantaneously informs you of ongoing sales on items you frequently purchase online—or scanning a QR code to find out if an item is in stock at a nearby location.
5. Advancements and Trends
With new AI tools continuing to evolve, AI agents are becoming more autonomous and more deeply embedded into business processes. Here are some emerging trends:
a) Greater Autonomy
As more sophisticated machine learning models come to fruition, “AI agents are expected to gain more advanced decision-making and reasoning capabilities, enabling them to operate with minimal human oversight.” This evolution could see AI agents tackling tasks that once relied heavily on human creativity and intuition, while we keep a watchful eye on how well these systems can handle unexpected edge cases.
b) Collaborative Multi-Agent Systems
In the near future, we might see multiple AI agents joining forces, each specializing in a particular skill. Together, they can swiftly solve problems that single-agent systems might struggle to handle alone. These teams of agents promise a new scale of efficiency, and “future systems may involve multiple specialized agents working harmoniously to solve complex problems.” Some companies are already experimenting with multi-agent strategies to break down large-scale tasks into smaller, simultaneously handled assignments.
c) Seamless Integration
We can expect AI agents to run “in the background” of business operations. As organizational processes are digitized, agents can connect to data streams, spot trends or anomalies, and automatically execute tasks. “AI agents may become increasingly embedded in business operations, automating workflows in the background.” An example might be an accounting AI agent that monitors expenses in real time, anticipating budget overflows before they become major issues.
d) Leveraging Foundation Models
An additional emerging development is that more AI agents are tapping into “foundation models,” which are large-scale machine learning models pre-trained on massive datasets. These foundation models can give AI agents a head start, helping them understand language better or recognize objects faster. This synergy pushes the capabilities of AI agents even further, allowing them to quickly adapt to new tasks or data types.
6. Challenges in Deployment
While AI agents hold tremendous promise, it’s important to understand the challenges that accompany their deployment:
1) Data Privacy
AI agents often rely on large amounts of user data. Organizations must “safeguard sensitive data collected and used by AI agents.” Failing to do so can lead to regulatory fines, reputational damage, and a loss of consumer trust.
2) Bias and Ethics
Because AI models can inadvertently learn biases from data, companies need to proactively check for fairness. “Ensuring fairness and accuracy in AI models is critical to avoid biased outcomes.” This calls for constant updates and thorough testing of AI systems to verify that they are making decisions based on ethical and equitable standards.
3) Technical Expertise
To build AI agents, technical know-how is essential. From machine learning to system integration, “building and managing AI agents require skilled developers familiar with machine learning and system integrations.” This skill gap may slow down the pace at which organizations adopt AI agents.
4) Resource Demands
Cutting-edge AI agents often require heavy computational resources and large quantities of data. “Advanced AI agents demand substantial computational and energy resources for training and operation.” This can be a major hurdle for companies lacking the budget or infrastructure to deploy cloud-based AI solutions at scale.
7. Conclusion
The AI agent stands at the forefront of artificial intelligence progress. It combines autonomy, adaptability, and intelligence in a manner never seen before, permeating industries and opening doors previously locked by time, cost, and complexity. From e-commerce to healthcare, finance to transportation, AI agents are quickly reshaping how we interact with technology—and perhaps just as importantly, how technology interacts with us.
By constantly learning, adapting, and refining its operations, the AI agent can deliver impressive outcomes. Whether it is a chatbot that cuts customer service calls by half or a manufacturing system that anticipates machinery failures, these “autonomous software systems” present a game-changing potential for improved efficiency and personalized user experiences. Indeed, “AI agents represent a significant evolution in artificial intelligence, combining autonomy, adaptability, and intelligence to transform industries globally.”
As we look ahead, AI agents may become even smarter and more independent—learning faster and collaborating across multi-agent systems to tackle complex tasks. They will likely integrate with existing workflows in the background, quietly and efficiently processing data, making decisions, and executing tasks. For businesses, this signals an era of continuous digital transformation with AI. For example, blending AI agents with robotic process automation could yield unprecedented results in operational efficiency. And for everyday consumers, these developments hint at more personalized, seamless interactions in our daily lives.
Of course, challenges remain—particularly around data privacy, ethical AI, specialized technical capabilities, and the resource demands these tools require. However, as the field matures and more robust regulations and best practices surface, these hurdles are likely to be addressed. In many cases, the benefits from AI agents far outweigh the risks, especially if organizations adopt them conscientiously.
Ultimately, if today’s trends continue, AI agents may evolve from novel “assistants” to key players in nearly all verticals worldwide. By harnessing machine learning, foundation models, and natural language interfaces, AI agents are growing in sophistication every day. Soon, they might proficiently manage the lion’s share of transactional tasks across a company’s operations, leaving humans to innovate, create, and tackle the strategic aspects of business. All told, the future of “AI agent” technology looks bright, and it’s certainly a story we will continue to follow with excitement and curiosity.
FAQ
Q: What exactly is an AI agent?
An AI agent is an autonomous software system designed to perceive, reason about, and act upon its environment in order to achieve specific goals. It relies on techniques such as machine learning, natural language processing, and advanced decision-making frameworks.
Q: Are AI agents going to replace human workers?
AI agents often excel at repetitive or data-heavy tasks, freeing people to focus on more creative, strategic, and interpersonal work. While they may automate certain job functions, they usually supplement rather than fully replace human roles.
Q: How do organizations get started with AI agents?
Companies typically begin small, identifying a high-impact use case where automation or decision-making can be improved. From there, they gather the necessary data, build or adopt a suitable AI model, and integrate the agent into existing workflows.
Q: What are the main risks with AI agents?
Key concerns include data privacy, ethical considerations, bias in algorithms, and the computational resources required to train and maintain these systems. Proper oversight, regular audits, and robust security measures can help mitigate these risks.
}