AI Agent: Transforming Tasks Through Intelligent Automation
AI Agent: Transforming Tasks Through Intelligent Automation
Estimated reading time: 12 minutes
Key Takeaways
- AI agents learn from and adapt to their environments, enabling true autonomy.
- They reduce human workload by handling repetitive and data-intensive tasks.
- Integration across industries—from healthcare to finance—is accelerating rapidly.
- Challenges include data privacy, bias, ethics, and computational complexity.
- Future developments promise more creative, generative solutions and broader accessibility.
Table of Contents
- Exploring the World of the AI Agent
- Overview of AI Agents
- Features and Principles of AI Agents
- Applications of AI Agents Across Industries
- Types of AI Agents
- Challenges and Concerns
- Leading Companies and Technologies
- The Road Ahead for AI Agents
- Conclusion: Embracing the Potential of AI Agents
- Previous Blog Posts
- FAQ
Exploring the World of the AI Agent
Imagine a computer program that can learn, make decisions, and complete tasks all on its own. That is the thrilling reality of the AI agent. AI agents exist in many forms, from simple systems that manage your room temperature to advanced cars that drive themselves through busy city streets. These agents are becoming more common everywhere, making life easier for people at work and at home. As we discover how AI agents work, we will see that they can change the world by saving time, improving efficiency, and even helping with medical tasks that were once too difficult for machines. Let us peek into how AI agents operate, why they matter, and what challenges and opportunities they bring along.
Overview of AI Agents
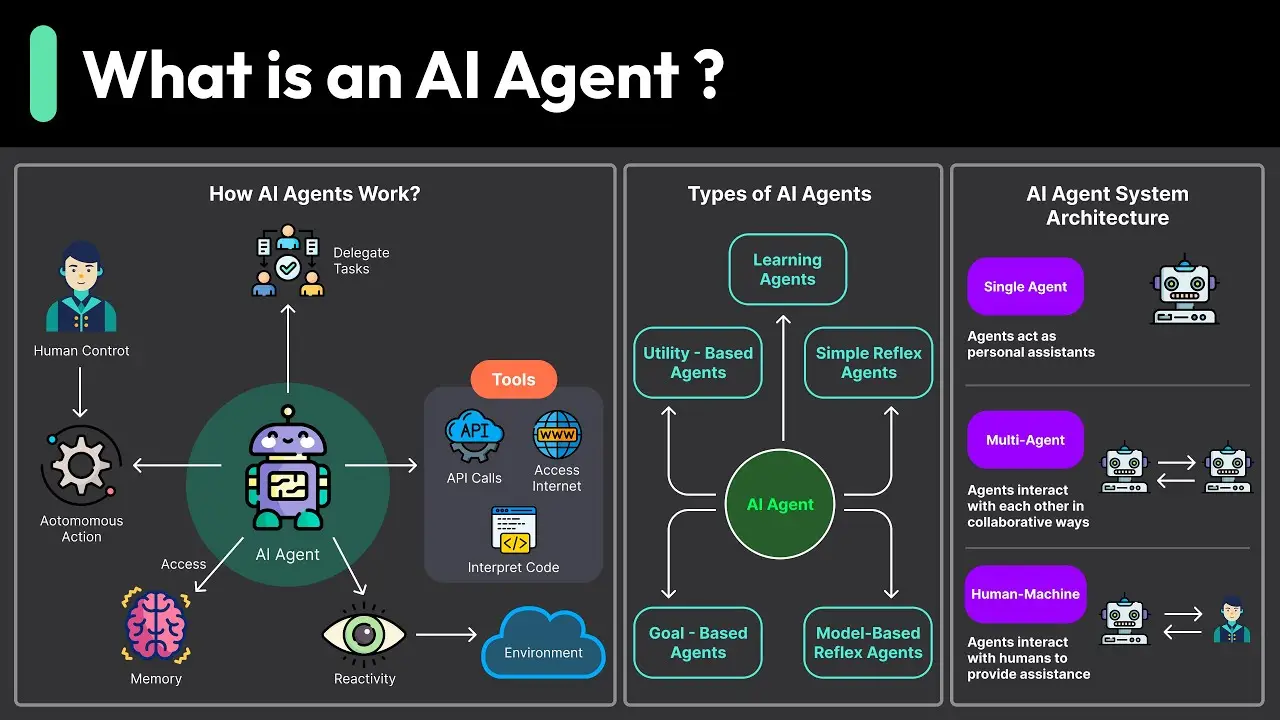
AI agents, also known as intelligent agents, are software programs built to perceive their environment, make decisions, and assess outcomes
(source;
source).
These programs rely on data, logic, and learning techniques to achieve goals. They can function independently, adjusting their plans, choices, and actions over time. When you set a thermostat to keep your room at a certain temperature, you can think of that as a very basic example of an AI agent. The thermostat senses the temperature and, without being told step by step, makes adjustments to the heating or cooling system.
But AI agents handle much more than home air conditioning. Some can read and understand huge amounts of data, like medical images or financial records, to find patterns and make accurate, real-time decisions. In self-driving cars, they track road conditions, manage movement, and constantly learn to improve safety. As tech companies continue to explore new uses, it is clear that AI agents are moving us toward a future with greater automation, better logistics, and more interesting and creative ways to solve problems.
Features and Principles of AI Agents
AI agents stand out because they operate on several important principles. Two major concepts are autonomy and rationality. Autonomy means that these agents do not always rely on human instruction. Instead, they use data and logic to optimize performance and results, striving for goals without needing constant human input
(source;
source).
For example, a chatbot can learn how to answer customer questions on its own, deciding the best reply based on previous user interactions.
AI agents also need to perceive and act upon the environment around them. This environment might be the physical world, captured through cameras and sensors, or it might be digital data gathered from customer inputs and online sources
(source).
Think about a robot in a warehouse: it has sensors to detect obstacles and a mechanical arm to handle goods. That robot’s AI agent “perceives” the location of objects and calculates how to move them efficiently.
Another crucial factor is adaptability. Advanced AI agents rely on iterative learning models, memory-based analyses, and a deeper understanding of measurable clues over time
(source;
source).
As an example, a predictive maintenance system in a factory will record how machines behave, compare new data to stored information, and spot warning signs faster. The agent learns from historical changes so that it can detect potential breakdowns before they happen.
Most importantly, AI agents must be goal-oriented. They are designed to follow set goals, break larger tasks into smaller steps, and measure ongoing progress
(source;
source).
A goal for a self-driving car could be “Drive from A to B safely,” which involves subgoals like “avoid collisions,” “follow traffic rules,” and “take the best route.” By staying focused on these clear targets, AI agents can gradually improve their precision and reliability.
Applications of AI Agents Across Industries
AI agents have found their way into many areas of business and life. They bring big improvements in efficiency, decision-making, and making people’s lives easier. Below are a few important sectors where AI agents take charge.
1. Customer Service and Marketing
Customer support is one of the biggest fields where AI agents are making a difference. Chatbots and virtual assistants can run day and night, helping people with orders, returns, product advice, and password resets. A prime example is Amazon using AI to guide shoppers. Another is Chatbase, which saw a 65% drop in support tickets after adding AI agent technology to handle all sorts of queries
(source;
source).
This means service teams can be more productive, since AI agents handle everyday questions quickly. For more on enhancing business efficiency with AI, check out
AI Tools for Small Business.
2. Healthcare
In healthcare, AI agents assist in everything from diagnosing diseases to suggesting treatments. They can look at big sets of medical images or lab results, flagging dangerous clues that doctors might miss on their own. For example, Google has developed an AI agent that surpassed dermatologists with an 85.4% accuracy in diagnosing skin cancer
(source;
source).
This can bring life-saving improvements by catching illnesses early. Healthcare AI agents also support robotic surgeries, which allow for more precise operations with potentially fewer mistakes.
3. Manufacturing
AI agents play a vital role in making factories smarter, safer, and more efficient. Many manufacturing plants use predictive maintenance systems to monitor equipment around the clock, spotting subtle changes in performance that could indicate wear or a looming breakdown. Siemens, for instance, discovered that with the help of predictive AI, they could cut downtime by 40% and boost productivity by 10%
(source).
These AI tools look at vibrations, sounds, and many other signals to recognize problems before they grow, saving both time and money.
4. Autonomous Vehicles
When it comes to self-driving cars, AI agents are at the heart of the show. They gather real-time data from radar, cameras, and lidar to detect obstacles, read traffic signs, and plan routes safely. Waymo is one company using model-based AI agents to deploy driverless cars in major cities like Los Angeles and Phoenix, hoping to transform transportation itself
(source).
As these systems learn and improve, the potential for safer roads increases, cutting down on accidents and gridlock.
5. Finance and Cryptocurrency
Detecting fraud, assessing credit applications, and optimizing large portfolios are all tasks suited to advanced AI agents. By studying patterns in financial transactions, these systems spot suspicious activity fast, blocking potential fraud before it can escalate. JP Morgan, for example, cut fraud by 70%, which helped save $200 million a year using AI
(source;
source).
This technology also assists in cryptocurrency markets, where AI agents learn from market fluctuations and help traders develop more informed strategies.
6. Energy and Chemical Industries
In the race toward sustainable power and efficient production, AI agents assist plants and systems by monitoring equipment integrity, coordinating complex chemical processes, and even optimizing solar panel layouts
(source;
source).
These agents study data from sensors that measure temperature, pressure, or chemical concentration, adjusting in real-time to ensure the safest and most efficient operations. By foreseeing failures or minor leaks, companies can save money while reducing environmental harm.
Types of AI Agents
AI agents are not all alike. We can roughly group them by how advanced they are and how they function. Four common kinds are simple reflex agents, model-based agents, utility-based agents, and learning agents
(source;
source;
source).
1. Simple Reflex Agents
These are the most straightforward type. They look at the environment and respond according to fixed rules or triggers. A thermostat is an easy example. When the temperature dips below the set threshold, it knows to turn on the heat. These agents do not remember past conditions or predict future outcomes; they simply react
(source;
source).
2. Model-Based Agents
Model-based agents build some form of internal representation or model of their environment. They track past observations and try to predict future states, helping them decide what action to take next. Self-driving cars are a perfect example of model-based agents. They need to know road layouts, traffic patterns, or pedestrian movements, using data from cameras, radar, and more. The car’s model helps it forecast potential hazards like sudden stops or lane changes
(source;
source).
3. Utility-Based Agents
These agents look at possible actions and choose the one that maximizes a desired outcome, like profit or efficiency
(source).
Imagine how a ride-hailing service might adjust fares using an AI agent: the system predicts supply and demand in certain areas and changes prices to find the best balance. By attaching a number (or “utility”) to outcomes, the agent picks the action that brings the highest utility score in that moment.
4. Learning Agents
Learning agents dig deeper, constantly improving their performance by gathering feedback from their actions. Recommendation engines, like those found in Netflix or YouTube, fall under this category. They look at user behavior to figure out what each person might like, adjusting suggestions as new data arrives
(source).
In time, these agents become more accurate, turning repeated interactions into sharper knowledge about patterns and preferences.
Challenges and Concerns
AI agents can be breathtaking in their possibilities, but they also come with challenges. Data privacy is a hot concern today. Since AI agents gather lots of user data, from personal details to browsing history, storing this information properly is crucial. Big data sets can become magnets for hackers or be used improperly without the right safeguards
(source;
source).
Another important topic is bias and ethics. If the data feeding an AI agent is skewed or lacks diversity, the agent could produce unfair or potentially harmful decisions
(source).
For instance, a financial AI agent may deny loans to certain groups more often if its training data contains unbalanced patterns. Ensuring fairness and responsible use requires human oversight, smarter data collection, and ongoing monitoring.
Computational complexity is yet another hurdle. AI agents might require specialized hardware, large data sets, or advanced knowledge in data science and machine learning to set up and keep running
(source;
source).
Small businesses, nonprofits, or institutions with limited resources must weigh the cost of implementing AI agents so that they do not create technology gaps. Cloud computing services help reduce some of these barriers, but careful planning is still essential.
Leading Companies and Technologies
Many technology giants and niche startups push AI agents to new heights. One prime example is Teneo, a company offering customizable AI agents for different industries such as healthcare, telecommunications, and retail
(source).
These AI solutions can be tailored to each business, ensuring that the agents speak naturally with customers, manage requests, and learn continuously.
HubSpot and Zoho are other top contenders, especially for customer relationship management (CRM). Both integrate AI agents to streamline sales and boost customer engagement, helping businesses track leads, set up promotions, and automate workflows
(source).
With advanced data analysis, these platforms provide more personalized experiences for customers and reduce manual tasks for staff. For comprehensive insights on workflow automation, visit
Workflow Automation Basics.
Waymo and Tesla have become practically household names in the self-driving world. Their advanced AI agents handle complex roadside conditions, with an eye toward making fully autonomous driving a common reality
(source;
source).
This leap involves billions of miles of driving data, carefully crafted models, and evolving regulations to ensure safety. Autonomous travel is still in the works, but its steady progress shows how AI agents are transforming transportation.
The Road Ahead for AI Agents
The rise of the AI agent leads us to an exciting future filled with possibility. In the near term, we can expect AI to handle more complex tasks at greater scales with improved speed. Breakthroughs in machine learning and deep learning techniques, such as transformers and large language models, are allowing AI agents to understand speech, process images, and even generate entire essays more effectively than ever before. These improvements hint at a future in which AI agents can act like helpful, knowledgeable teammates in nearly any area, from writing and design to complex problem-solving in biomedical research.
Generative AI also pairs well with AI agents, leading to tools that can craft new product designs, draft marketing copy, or even offer imaginative solutions to problems that humans have not yet considered. Combining generative AI’s creativity with the adaptability of AI agents may mean more original, dynamic products and services. This will especially catch the eye of industries like entertainment, education, and marketing, where creativity and the ability to keep users engaged are vital. To explore the leading AI agents transforming industries, refer to
Exploring the Impact of AI Agents.
Yet, even with all this promise comes an obligation to tackle important questions: Are we ensuring AI agents remain fair and ethical? How do we broaden access so that small communities and low-budget organizations can also benefit from these advancements? Policymakers and technologists must join forces to find a balanced way forward, setting the stage for healthy growth and sharing success evenly.
Conclusion: Embracing the Potential of AI Agents
The AI agent is no longer a far-off dream—it is here, changing how we work, how we travel, how we shop, and how we get healthcare. From basic programs like thermostats to futuristic self-driving cars, AI agents have proven effective at automating tasks, learning from mistakes, and finding novel ways to solve problems. Because they can gather and study data so well, these agents reshape the way industries make decisions, all while freeing humans to focus on the bigger picture and more creative tasks.
Grounded by the principles of autonomy, perception, adaptability, and a clear focus on goals, AI agents are now in customer service, finance, retail, and even energy. By applying these systems in strategic ways, companies can cut expenses, scale up faster, and deliver better results to clients. At the same time, it is vital that leaders, developers, and the public address privacy and ethical questions. Fairness, transparency, and security are absolute musts, especially when AI agents are making decisions that affect people’s safety or financial futures.
The path forward involves making sure that AI agents remain tools for good, powered by strong oversight, diverse and balanced training data, and clear rules on how they should work. The future of AI agents is about pushing the limits of technology, but it is also about making sure we do it responsibly and fairly. With that in mind, we stand on the edge of a breathtaking revolution, where machines learn, adapt, and help us unlock a world of comfort, efficiency, and new discoveries.
As we keep researching and adopting AI agents, excitement will only keep growing. New companies will enter the space, new applications will arise, and the global AI community will keep fine-tuning and expanding what is possible. From checking you into your next flight to designing solar energy systems that pick up on little shifts in weather, these agents will touch all facets of our lives sooner than we think. The AI agent is more than just a buzzword—it is a powerful technology changing our world, one step at a time.
Previous Blog Posts
-
Best AI for Business in 2025: Tools and Trends You Need to Know
Keywords: best ai for business
https://bizioffice.com/best-ai-for-business-2025 -
AI Tools for Small Business: Growing Your Company with Smart Technology
Keywords: ai tools for small business
https://bizioffice.com/ai-tools-for-small-business -
Workflow Automation Basics: A Comprehensive Guide for Streamlining Your Business Operations
Keywords: workflow automation basics, benefits of workflow automation, workflow automation for SMBs, business process automation, digital workflow management
https://bizioffice.com/workflow-automation-basics-guide -
Harnessing the Power of AI Workflow Automation
Keywords: I workflow automation, AI process automation, machine learning for business workflows, AI-driven workflow design, intelligent automation for small business
https://bizioffice.com/ai-workflow-automation-insights -
Unleashing the Power of AI Agents: Transforming Industries and Introducing Autonomous Intelligence
Keywords: ai agent
https://bizioffice.com/ai-agent-autonomous-helpers -
Mastering Workflow Automation Implementation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Keywords: workflow automation implementation, workflow design best practices, custom workflow automation solutions, seamless automation integration, optimizing business processes with AI
https://bizioffice.com/mastering-workflow-automation-implementation -
Exploring the Impact of AI Agents: Revolutionizing Modern Industries and Everyday Life
Keywords: ai agent
https://bizioffice.com/exploring-ai-agent-technology -
Best Workflow Automation Software: Comprehensive Guide to Optimize Your Business Operations
Keywords: workflow automation basics, benefits of workflow automation, workflow automation for SMBs, business process automation, digital workflow management
https://bizioffice.com/2025/04/08/best-workflow-automation-software-guide/
Frequently Asked Questions
-
Q: What exactly is an AI agent?
A: An AI agent is a software program that can perceive its environment, make decisions, and execute tasks independently. It leverages data and learning models to adapt over time.
-
Q: How do AI agents learn and improve?
A: Many AI agents incorporate machine learning, storing data and analyzing feedback from past actions. They refine their strategies, becoming more accurate or efficient with each iteration.
-
Q: What are common challenges when implementing AI agents?
A: Data privacy, ethical biases, and computational costs are major concerns. Proper safeguards, diverse training data, and transparent processes help mitigate these issues.
-
Q: Can small businesses benefit from AI agent technology?
A: Absolutely. AI agents can automate routine tasks, improve customer service, and assist in data analysis. Cloud-based solutions often make these systems accessible without huge infrastructure costs.
}