AI Agent: Transforming Workflows and Industries
AI Agent: The Rising Star of Intelligent Automation
Estimated reading time: 8 minutes
Key Takeaways
- AI agents autonomously perceive their environment, make decisions, and execute tasks to pursue goals.
- They’re already transforming industries from e-commerce to healthcare, often reducing costs and improving productivity.
- Data privacy, ethics, and compute requirements remain key challenges.
- Future trends include multi-agent collaboration, hyper-personalization, and self-improving systems.
Table of contents
- AI Agent – Transforming Workflows and Industries
- What Is an AI Agent?
- Core Features of AI Agents
- Types of AI Agents
- AI Agents vs. Other AI Technologies
- How AI Agents Work
- Real-World Applications of AI Agents
- Industry Impact and Emerging Trends
- Key Challenges for AI Agents
- The Future Outlook
- Conclusion
- FAQ
AI Agent – Transforming Workflows and Industries
Welcome to this week’s most trending news in AI, where we’ll dive into the rapidly evolving realm of the AI agent. Right now, the concept of an AI agent stands at the forefront of cutting-edge technology. Its capabilities and promise have stirred excitement in industries and research communities worldwide. From self-driving cars to customer support automation, AI agents are opening up thrilling possibilities. This post explores everything from their definition and core concepts to their real-world applications, challenges, and the future paths they’re blazing. Let’s jump right in.
What Is an AI Agent?
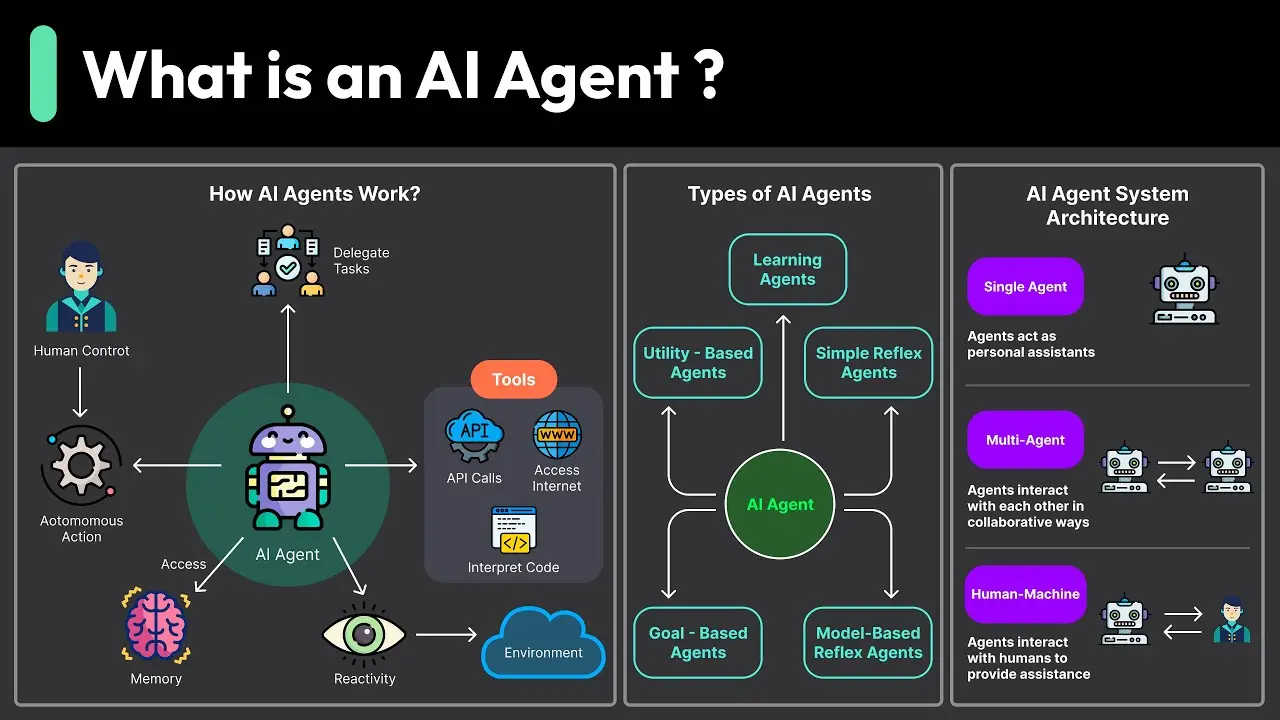
An AI agent, by definition, is an autonomous software program or system that perceives its environment, makes decisions, and executes actions to pursue a specific goal
(source),
(source),
(source),
(source),
(source). This means it can gather data from various sources, analyze the information, plan multiple tasks, and use tools like APIs or databases to achieve a set goal—all without needing someone continuously watching over it.
A key concept behind an AI agent is that it’s a rational agent
(source),
(source),
(source). “Rational” doesn’t necessarily mean perfect; instead, it implies that the agent aims to maximize its performance according to how it’s programmed. For instance, if the agent’s task is to improve customer satisfaction, it’ll learn to optimize the solutions that lead to higher satisfaction scores. It doesn’t just react to what’s happening but also learns from feedback, thinks ahead, plans, and evolves in strategy
(source),
(source),
(source).
Core Features of AI Agents
1. Autonomy
AI agents operate independently, making decisions without someone needing to hold their hand and watch over them all the time
(source),
(source),
(source). They receive a goal, and then they use built-in logic and algorithms to pursue it.
2. Perception
These agents perceive the environment in various ways, which can range from sensors (in robotics) to inputs from users or data streams
(source),
(source),
(source). Think of your phone’s voice assistant collecting your voice commands and converting them into text—it’s perceiving what you say.
3. Reasoning and Planning
Reasoning is a crucial step for AI agents. They break down their goals into actionable tasks or instructions, figure out sequences, and plan how best to get from point A to point B
(source),
(source),
(source). For instance, if you ask an agent to schedule a set of business meetings, it may check multiple calendars, look for open slots, handle location issues, and piece together an efficient plan.
4. Learning and Adaptation
Today’s AI agents learn from tasks they accomplish, from successes and failures, and from user feedback
(source),
(source),
(source). This means they can sometimes catch their own mistakes and correct them on the fly.
(reference)
5. Tool Use
AI agents don’t always rely solely on their internal programming. They can draw upon external resources like search engines, databases, or even other specialized AI services if they lack certain knowledge or need specific functionality
(source),
(source).
Types of AI Agents
AI agents come in a variety of forms, each suited for particular tasks and environments
(source),
(source),
(source),
(source). Here’s a handy overview:
1. Simple Reflex Agents
These agents base their actions purely on current inputs and preset rules, with no learning involved. A typical example is a basic thermostat that turns the heat on or off depending on the temperature. There’s no memory of what happened before.
2. Model-Based Reflex Agents
These agents keep track of certain internal states and can handle partially visible situations. A good example is a context-aware chatbot that remembers parts of your conversation and uses that memory to guide future responses.
3. Goal-Based Agents
This category is always looking for ways to achieve a specific goal. An example is a robotic navigation system that seeks to reach a particular destination. It considers the environment, calculates possible paths, and chooses the most suitable route.
4. Utility-Based Agents
Sometimes it’s not enough to just achieve a goal; you want to achieve it in an optimal way. Utility-based agents maximize certain performance metrics. We see this in dynamic pricing systems that set prices to maximize profits or in self-driving cars that try to optimize safety, fuel usage, and travel time.
5. Learning Agents
These agents adapt continuously and get smarter with each interaction. Think recommendation systems that start with basic recommendations, then refine and personalize suggestions based on what you watch or click.
6. Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
Multi-agent systems involve multiple agents working together toward shared goals, such as collaborative robots in a factory, each performing different tasks that contribute to the overall production process.
7. Hierarchical Agents
Sometimes tasks are so big that you need multiple layers of organization. Hierarchical agents address this by dividing tasks and assigning them to sub-agents. You could see this in supply chain management, where different tiers focus on procurement, transportation, distribution, and so on.
AI Agents vs. Other AI Technologies
It’s easy to get lost in the maze of AI-related jargon—assistants, chatbots, AI models—so let’s draw a simple comparison
(source),
(source):
- AI Agents: Act autonomously, solving goals, learning, adapting, and even using other tools as needed.
- AI Assistants: Assist humans by interacting with them, typically requiring more direct supervision.
- Chatbots/Bots: Usually designed for straightforward interactions, often rule-based and limited to specific tasks.
- AI Models: Typically produce predictions or classifications based on data; not autonomous by themselves.
How AI Agents Work
The workflow of an AI agent can be broken down into these steps
(source),
(source),
(source),
(source):
1. Goal Setting
You, as the user, specify what the agent should achieve. Maybe you tell it, “Book the next available flight to New York for under $400.”
2. Task Planning
Next, the agent figures out how to solve it. That could involve checking certain data sources, scheduling tasks, or using external APIs.
(reference)
3. Information Gathering
The agent finds information that’s relevant to its goal. It might scrape websites, scour databases, or collaborate with other agents or specialized AI systems.
4. Execution
With a plan in hand, the agent takes action—scheduling appointments, placing orders, analyzing images—whatever the goal demands.
5. Feedback and Learning
AI agents are never quite finished. They observe how well everything went and adapt for future performance. The agent ideally becomes better at anticipating pitfalls or discovering improved strategies.
Real-World Applications of AI Agents
AI agents aren’t just fascinating in theory. They’re already operating in many fields, boosting efficiency, saving time, and opening new avenues of possibility.
1. E-Commerce
With so much buying and selling happening online, AI agents help by generating personalized recommendations and managing order logistics
(source),
(source). For example, Amazon’s recommendation engine uses data on past purchases and browsing habits to suggest items you might like.
(reference)
2. Customer Support
AI agents can process refunds or troubleshoot basic queries. According to Chatbase, some AI agent deployments have reduced support ticket volumes by 65%
(source),
(source). Human experts then handle more complex or sensitive issues.
3. Sales & Marketing
Sales teams use AI agents to identify leads and personalize campaigns
(source). Solutions like Find AI and AgentForce conduct outreach and deliver targeted messaging.
4. Healthcare
Systems analyzing medical images or assisting in surgeries can detect patterns doctors might miss
(source),
(source),
(source). Google’s AI for skin cancer diagnoses has shown accuracy exceeding many practicing dermatologists.
5. Finance
From fraud detection to automated investment advice, AI agents help spot risks and act fast
(source),
(source). Major institutions use these systems to scan massive transaction pools and flag suspicious activity.
6. Manufacturing
In factories, AI agents coordinate predictive maintenance, quality control, and inventory management
(source),
(source). Siemens, for example, has cut downtime by 40% using such technologies.
7. Autonomous Vehicles
Self-driving cars process sensor data, interpret road conditions, and make decisions in real time
(source),
(source). Multiple sub-agents handle navigation, collision detection, and route planning.
8. Dynamic Pricing
Companies like Uber use AI agents to adjust prices based on real-time conditions
(source),
(source). When demand spikes, prices go up, and vice versa.
Industry Impact and Emerging Trends
1. Hyper-Personalization
AI agents push personalization far beyond simple product recommendations, mining data signals to adapt experiences to each individual
(source).
2. Self-Improving Systems
Some AI agents can detect and fix their own performance gaps, autonomously updating their algorithms
(source).
(reference)
3. Multi-Agent Collaboration
Rather than relying on a single omniscient agent, multiple specialized agents can coordinate to solve complex problems
(source).
(reference)
4. Market Growth
Experts predict the global market for autonomous AI agents will grow from $4.8 billion in 2023 to $28.5 billion by 2028
(source). Companies see big opportunities in investing in agent technology.
Key Challenges for AI Agents
1. Data Privacy
AI agents require extensive data to work effectively, raising concerns about misuse or leakage
(source).
2. Ethics and Fairness
Algorithms can inadvertently adopt biases from their training data, perpetuating inequalities
(source). Proper oversight is crucial.
3. Technical Complexity
Advanced AI agents demand sophisticated software, vast data pipelines, and robust infrastructures
(source),
(source).
4. Compute Resources
More complex tasks require powerful hardware, which can be expensive and often necessitates specialized cloud solutions
(source).
(reference)
The Future Outlook
As AI agents become more integrated into daily workflows, several paths for evolution stand out:
• Proactive, Context-Aware Assistance
Imagine an AI agent preemptively reallocating resources on a project if it detects a likely delay
(source),
(source).
• Greater Adoption in Regulated Industries
Better ethics and accountability frameworks will encourage the use of AI agents in sensitive fields like healthcare, finance, and government.
• Seamless Integration with Physical Devices
Agents will increasingly coordinate with robots, drones, and IoT devices, bridging digital and physical domains.
• Multi-Agent Collaboration for Complex Problems
We’ll see more networks of specialized agents tackling challenges too big for any single system.
Conclusion
AI agents represent a monumental leap in how we use technology to automate and improve our lives. Gone are the days when “automation” simply meant following a single predictable script. Today, an AI agent can learn, adapt, and even discover new strategies to tackle problems more efficiently. Sectors ranging from e-commerce to healthcare have already adopted AI agents, and forecasts pegging the market at over $28 billion in a few years
(source) underscore just how transformative they can be.
Challenges such as data privacy, bias, and hardware resources remain, but they are fueling innovation in safer, fairer, and more robust systems. Whether you’re an entrepreneur looking to streamline operations or a casual observer sensing a seismic shift in tech, keep an eye on AI agents. With autonomy, adaptability, and the ability to collaborate, they’re turning what was once science fiction into a rapidly evolving reality.
FAQ
1. Are AI agents the same as chatbots?
Not necessarily. Chatbots often follow strict rules and workflows, whereas AI agents operate autonomously, make decisions, and can learn over time.
2. What’s the difference between an AI assistant and an AI agent?
AI assistants may need more direct supervision—like clarifications or approvals—while AI agents can make decisions and act on goals with minimal human input.
3. Will AI agents replace human workers?
They automate repetitive and data-intensive tasks, but they also create new opportunities and roles. Complete replacement isn’t the most likely scenario; rather, they’ll augment human capabilities.
Safety depends on proper design, data governance, and testing. As with any tech, ethical implementation and ongoing oversight are key to minimizing risks and biases.
}