Agents in AI: Transforming Autonomous Technology and Real-World Applications
Agents in AI: The Next Frontier of Autonomous Technology
Estimated reading time: 10 minutes
Key Takeaways
- AI agents are software programs capable of sensing, deciding, and acting on their own.
- They can be simple rule-based systems or advanced solutions powered by large language models.
- Integration with tools and APIs allows AI agents to perform real-world tasks.
- Many industries—healthcare, customer service, logistics—already rely on these autonomous systems.
- Ethical design and handling novel situations remain key challenges.
Table of contents
- 1. Introduction
- 2. What Are AI Agents?
- 3. Core Capabilities of AI Agents
- 4. Exploring Types of AI Agents
- 5. Modern AI Agents and LLMs
- 6. Real-World Applications of AI Agents
- 7. Advantages and Challenges
- 8. AI Agents in Action: A Day-in-the-Life Scenario
- 9. Why Are LLM Agents So Important?
- 10. The Road Ahead: Emerging Trends
- 11. Summary: AI Agents Poised for Impact
- 12. Frequently Asked Questions
Agents in AI: Exploring Their Role and Capabilities
Have you ever wondered how computers can learn on their own and take actions without our direct control? That is the power of “agents in AI.” These special programs can see what is happening around them, make choices, and then do tasks all by themselves. Today, we will look at how AI agents work, why they are so popular, and the many ways they are changing our world. We will also discover how the rise of large language models (LLMs) has helped create a new type of AI agent with amazing abilities. By the end of this blog post, you will see why many experts say that AI agents are the next frontier of autonomous technology.
1. What Are AI Agents?
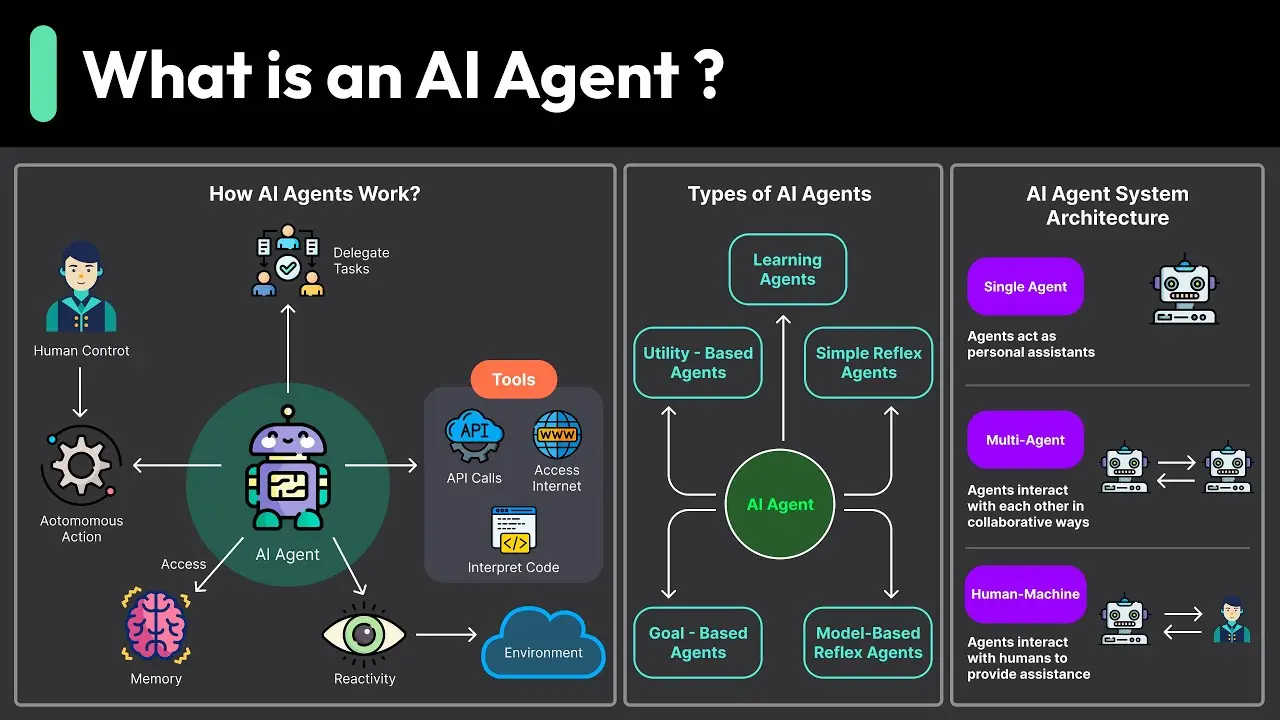
AI agents are software programs that can act on behalf of users or other systems. They receive input from their surroundings through sensors, process that information, make decisions, and then perform certain tasks. This means they can notice changes in their environment and respond in ways that help them reach their goals. According to IBM, an AI agent can be as simple as a program with rules or as advanced as one that uses large language models to learn and adjust over time. For more insights, visit AI Agent Intelligent Automation. Another IBM resource points out that these agents may even be able to use reasoning to figure out solutions for complicated problems. Check out this reference for more on advanced AI agents.
AI agents can be found working on everything from small office tasks to big industrial operations. They can connect with other tools, services, or systems. When they connect, they gain the power to do more complex things, such as pulling data from different sources, controlling devices, or even offering suggestions for improvements. As stated by Automation Anywhere, AI agents can handle numerous dynamic tasks in both digital and physical settings.
2. Core Capabilities of AI Agents
AI agents can do many impressive things. They do not just gather information; they can also learn and grow from past experiences. Based on data from IBM and Automation Anywhere, here are some of their key abilities:
- Autonomy:
They can do tasks and run workflows without needing constant human help. This might involve checking for new information, reading and writing data, or executing certain steps in a process (source). - Environment Interaction:
Agents often work in different environments—some might be digital spaces like computer networks, while others might be physical worlds with sensors and motors. For example, a robotic vacuum can move around your living room, scanning for dust and adjusting its path to avoid furniture. - Decision-Making:
AI agents can observe what is happening and decide the next best step to take. For instance, if a server monitoring agent sees that a network is very busy, it can decide to divert traffic or send alarms to human operators. - Learning and Adaptation:
Advanced AI agents can gather new insights from real experiences. Then, they can change their actions so that they perform better over time. A recommendation engine, for example, may learn more about what people like and suggest new items that fit their preferences. - Tool and API Integration:
Many agents can link with outside tools to increase their capabilities. For instance, a help desk chatbot might connect to a company’s database to find up-to-date product details and give accurate answers to user questions (source).
3. Exploring Types of AI Agents
Not all AI agents are the same. Some just follow simple rules, while others are advanced enough to learn from experiences and support large-scale tasks. According to resources from Amazon Web Services, IBM, and Automation Anywhere, we can group AI agents into several categories:
- Simple Reflex Agents
- Description: These agents take actions based on what is happening right now. They do not remember what happened before.
- Example: A thermostat that reacts to the temperature in a room. It turns heat on or off based on a single rule: If it is too cold, turn up the heat.
- Model-based Reflex Agents
- Description: These use an internal view or “model” of the world. This means they remember some of what happened before to make better decisions.
- Example: A robotic vacuum cleaner that keeps track of which rooms it has already cleaned.
- Goal-based Agents
- Description: They pick actions based on a desired goal. They think ahead, figure out which steps will help them meet that goal, and then act.
- Example: Automated route-planning software that finds the quickest way to deliver goods from a warehouse to a retail store.
- Utility-based Agents
- Description: These agents have a “utility function” that helps them measure which action is the best among different choices.
- Example: A dynamic pricing system for an online store. It finds the best price for a product at each time of day to get the highest profit while keeping customers happy.
- Learning Agents
- Description: These agents rely on their experiences. Their performance may improve as they gather more data or encounters.
- Example: A video-streaming recommendation agent that offers more tailored movie or TV show picks over time.
- Multi-Agent Systems (MAS)
- Description: Here, multiple agents make a team. They talk to each other, share tasks, and tackle big problems together.
- Example: A whole fleet of large delivery drones. Each drone works alone, but all drones share data and coordinate to ensure packages arrive safely to customers. For more on this, click here.
4. Modern AI Agents and LLMs
One of the most exciting developments in the AI world is the growth of Large Language Models (LLMs). These are powerful computer models able to handle very big tasks in natural language. They can write responses that seem quite human-like. As IBM and Automation Anywhere point out, these new LLM agents can understand everyday speech, store memories, and learn by taking in feedback. For further reading, see Unleashing the Power of AI Agents.
Imagine you want a single AI agent that can schedule your meetings, order your groceries, and even suggest fun weekend activities for you and your family. If it has a large language model at its core, it can understand your questions and instructions in a very natural way. Also, it can break down your larger requests into smaller tasks. For instance, if you say, “Hey, find me a dinner recipe with spinach and mushrooms,” the LLM agent can search recipes online, check your pantry inventory, and suggest the dish that uses ingredients you already have. The agent can even set a timer once you start cooking.
Modern AI agents do not just react; they can also reflect. They remember what they did and how you responded. If you said the spinach-mushroom recipe was too spicy last time, an LLM agent might suggest a milder option next time. This is all thanks to the agent’s ability to recall past interactions. Over time, as you keep sharing feedback, the agent becomes more in tune with your tastes.
These new AI agents usually connect to tools through application programming interfaces (APIs). This means they can do real-world tasks. For example, an agent that sees your fridge is almost empty can place a grocery order through an online store and schedule a delivery.
5. Real-World Applications of AI Agents
AI agents are not just science fiction. They are in use across many industries.
- Customer Support Chatbots
Many companies now have AI chatbots on standby to answer customers’ questions. According to Salesforce, these chatbots can look up orders, suggest solutions, or give instructions on how to fix problems. Customers save time, and support teams can focus on more difficult requests. - IT Automation
Large firms use AI agents to watch over servers, detect any unusual changes, and fix issues. According to IBM, if a server runs out of memory or acts strangely, an AI agent can quickly send alerts or reboot the system to avoid downtime (source). - Autonomous Vehicles and Robotics
Self-driving cars are basically AI agents on wheels. They use cameras, radar, and GPS data to decide how to steer, when to accelerate, and when to brake. They must adapt to their environment and avoid dangers. Robotic arms in factories are also guided by AI systems that learn how to assemble goods faster and safer each day. - Smart Home Controls and Device Automation
Many homes now have smart lights, locks, thermostats, and speakers. Some of these devices include AI agents that learn your behavior. For example, the system might know you usually watch TV at 7 p.m. It can dim the lights and switch the TV to your favorite channel just before you walk into the living room. - Supply Chain and Logistics
In large warehouses, multi-agent systems can map out the best way to organize and distribute items. Drones and AI robots communicate with each other to find the quickest routes and prevent collisions. This is especially important in giant e-commerce hubs where thousands of packages go out each hour. - Personalized Recommendation Engines
Online shops, streaming services, and news portals all use AI agents to predict what you like. Automation Anywhere notes that these recommendation engines gather information about your preferences and browsing history. They show you recommended books, videos, or even clothing that matches your style.
6. Advantages and Challenges
AI agents come with exciting advantages. However, they also introduce new problems that must be solved.
Advantages
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks:
AI agents can free humans from tasks that are dull, time-consuming, or prone to mistakes. - Scalability:
Since AI agents can work around the clock and do not get tired, they can help businesses serve many customers at once. - Self-Improvement:
Learning agents get smarter with time. This means they can fix their own mistakes and become better at serving users.
Challenges
- Novel or Ambiguous Situations:
Sometimes, an agent might come across a situation it has not seen before. If it has not learned how to handle it, the agent might fail or make a flawed decision. - Safe, Reliable, and Ethical Behavior:
AI agents need to be built to avoid harm, protect privacy, and follow laws. Design teams must make sure that these agents follow ethical guidelines. - Integration With Legacy Systems:
Older software or hardware can be hard for modern AI agents to connect with. Businesses may need to upgrade their technologies to support the new AI tools (source). For additional notes, see this guide.
7. AI Agents in Action: A Day-in-the-Life Scenario
Imagine you wake up in a smart home run by AI agents. Your smart speaker is already playing your favorite morning music. That is your personal AI agent at work. It knows from tracking your schedule that you have a busy day. It starts your coffee maker and adjusts your thermostat to a cozy temperature. As you sit down for breakfast, your wearable device shows a daily update of your health stats—your step count, last night’s sleep score, and how many calories you burned after that evening walk. An AI agent keeps track of these metrics to recommend better meal choices.
Next, as you drive to work in your semi-autonomous vehicle, the AI software inside the car checks traffic reports. It notices a big jam on the usual route and quickly plans an alternative path. While driving, you receive a message: your office’s help desk AI agent has found an IT issue on your computer and fixed it without bothering you.
When you reach your office, a separate AI agent might manage your emails, sorting them according to urgency and responding to routine inquiries. For example, if colleagues want to book time on your calendar, the agent finds open slots and sends confirmations. During lunch, it scans your local restaurants to see which dish best fits your dietary preferences. Then, at the end of the day, you sign off and head home. While you are on the way, your household AI agent turns on your HVAC system so the house is cozy by the time you arrive.
This simple scenario shows how AI agents can handle many different tasks in the background. They make your day easier, saving you time and mental energy for what matters to you most. For more details on this, visit Exploring AI Agent Technology.
8. Why Are LLM Agents So Important?
Large Language Models like GPT-like tools can do more than just respond to text prompts. With the ability to have conversations, they unify many features: searching the web, summarizing documents, recommending solutions, and more. When combined with an AI agent framework, these LLMs need less human guidance. They can track context, recall past queries, and learn your communication style. This transforms them from simple Q&A bots to full-fledged digital assistants or scenario managers.
For businesses, having an LLM-based AI agent means fewer overhead costs, faster responses to customer questions, and the ability to handle data from multiple sources. For an individual user, it might mean no longer needing to switch between multiple apps to plan a holiday or organize a party. Instead, you can chat with an AI agent that “gets you” and can handle the entire job from start to end.
9. The Road Ahead: Emerging Trends
We are still in the early stages of discovering all that AI agents can do. Here are some trends that might shape the future:
- Increased Collaboration Between Agents:
Expect multi-agent systems to grow. Multiple specialized agents will work together. A traveling agent might talk to a weather agent and a hotel-booking agent, each specialized in their own field. - Better Ethical Controls:
Researchers and developers are focusing on ways to ensure AI agents act ethically. They want agencies that are honest, protect privacy, and never discriminate or harm. - Wider Use Across New Fields:
AI agents could become part of education, medicine, and construction. Students may get personalized learning agents that adapt lessons based on their progress. In healthcare, agents might help doctors monitor patients at home to spot health warnings early on. - Real-World Robotics:
As robots get more advanced, we might see more AI agents working in real physical spaces—like drones delivering packages or robots caring for seniors.
10. Summary: AI Agents Poised for Impact
In summary, AI agents are software systems that can sense, think, and act to meet goals. They can be as basic as a simple program running on rules or as advanced as learning machines powered by giant language models. According to IBM and IBM resources as well as Automation Anywhere, these agents play a massive role in automation, cost savings, and improved customer service. LLM-based systems allow agents to understand natural language, recall information, and collaborate with real-world tools. As these systems grow more complex, they will tackle an even larger range of tasks—from managing warehouse robots to offering personalized recommendations for entertainment.
Yet, we must be aware of the challenges. AI agents can only handle what they have been trained on or designed for. When a brand-new problem appears, they might need help from human operators or new machine learning data to learn how to respond. Safety and ethics matter greatly too. Design teams need to ensure these technologies cause no harm and respect our shared values.
Over and over again, we see AI agents’ ability to transform business processes. They can talk to customers, fix server issues, and even manage the flow of robots on factory floors, all with minimal human input. Thanks to the rise of large language models, we can build agents that understand our questions, adapt to our preferences, and keep learning. This means that in the near future, many of our daily tasks may be handled by AI agents quietly working in the background. For more details on practical implementation, see Mastering Workflow Automation Implementation.
So the next time you notice your smart device adjusting itself to match your habits or see a quick response from a chatbot that feels almost human, remember that is an “agent in AI” going to work for you. As technology continues to move forward, we can look forward to even more exciting developments in this area. Who knows? We might soon have AI agents teaching us new skills, planning our travels, and even helping us create a better, more connected world. The potential is limitless, and the future looks bright for agents in AI!
11. Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the difference between an AI agent and a chatbot?
- Do I need coding experience to use AI agents?
- Are AI agents safe and reliable?
- Where can I learn more about AI agents?
What is the difference between an AI agent and a chatbot?
In general, a chatbot focuses on conversational interactions with users, often following scripts or limited decision trees. An AI agent can do far more, such as observing an environment, applying learning algorithms, and taking actions in both digital and physical spaces.
Do I need coding experience to use AI agents?
Not always. Many AI agents come in user-friendly platforms or are integrated into existing software. Non-technical users can often benefit from them without seeing a single line of code.
Are AI agents safe and reliable?
When designed with proper safeguards, AI agents can be very safe. However, unexpected inputs or novel situations can lead to errors. It is crucial to have both continuous monitoring and ethical constraints in place to ensure reliability and security.
Where can I learn more about AI agents?
Reputable tech blogs, research journals, and official documentation from providers like IBM, AWS, and Automation Anywhere are great places to start. You can also explore specialized resources like bizioffice.com for a deeper dive.
}